It can be a real challenge to 3D print with flexible filament on FDM 3D printers. This material is perfect for making DeLorean time machine tires and seat belts, dragon wings, clothes, capes and many other parts of 3D printing models. Gambody – Premium 3D printing marketplace wants to share tips for printing flexible filament. Follow our guide to make your new masterpieces look beautiful, boast all the intricate details and impress everyone with a masterful work.
In this detailed guide, you will find tricks on how to dry flexible filament, which settings to use while working with it, which is the best 3D printer for this type of material, etc.

Flexible Filament Types
3D printing material that bends and stretches is known as flexible filament. Hobbyists call such elastic filaments as TPEs. They are similar to rubber in their behaviour, and pretty popular among makers because they enhance the capabilities of a 3D printed model.
Here is an example of 3D printed flexible clothes that belong to Gandalf the Grey 3D printing figurine:
The TPE abbreviation stands for the Thermoplastic Elastomers. There are different types of TPE that have different chemical formulation and are distinguished by the degree of elasticity:
- TPU or Thermoplastic Polyurethane;
- TPC or Thermoplastic co-polyester;
- TPA or Thermoplastic polyamide.
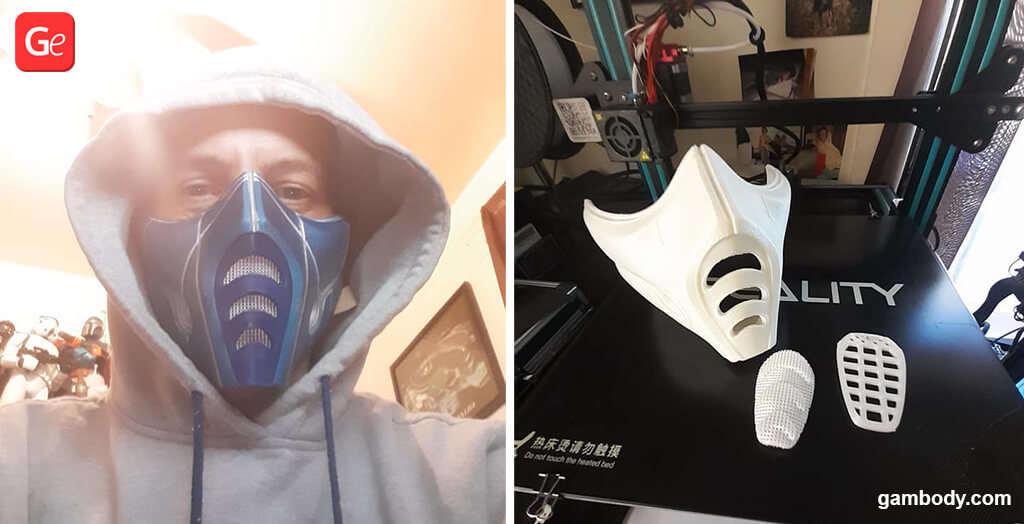
Some flexible filament types are perfect for 3D printing car tires and seat belts as in the DeLorean time machine model for 3D printing. They are also perfect for making fun 3D printing Face Masks:
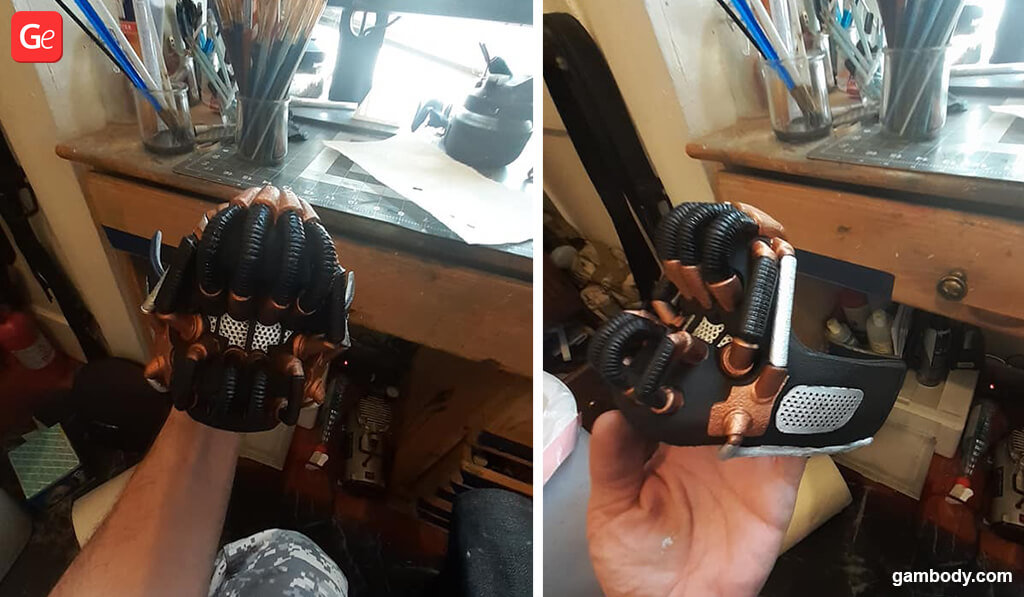


Others are good for creating rubber bands and similar parts of the models.
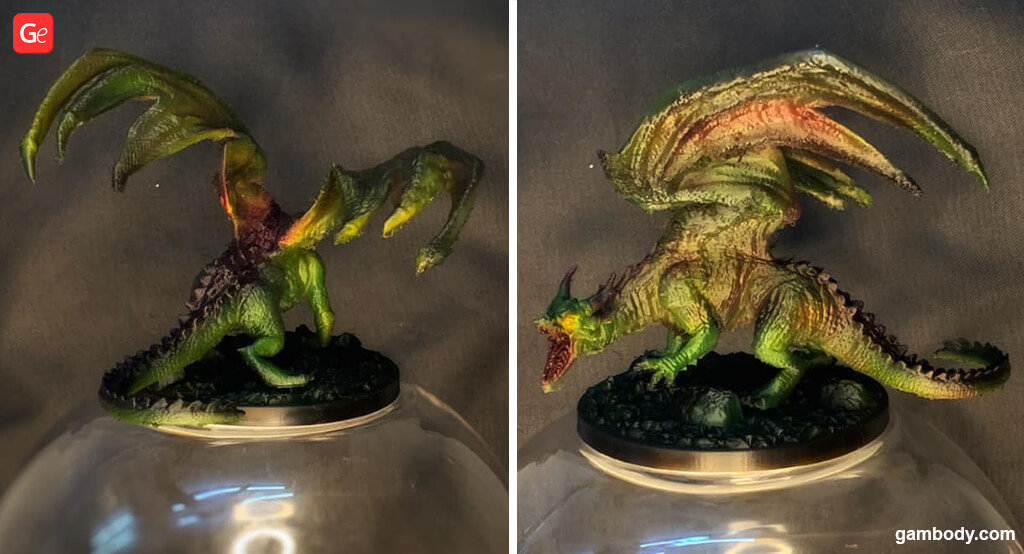

TPU is one of the most popular types of TPE among users with a 3D printer. And just like all other types of flexible filament, it has both advantages and disadvantages.
Its advantages are:
- Extended shelf-life;
- Softness and elasticity;
- Impressive impact resistance;
- Perfect vibration dampening.
Most common flexible filament problems:
- A real challenge to 3D print because the material is very soft;
- Bad bridging features;
- Not well suitable for Bowden extruders;
- Sizzled and popped-up 3D prints if TPE filament is not stored correctly (because TPE absorbs moisture);
- Risks of blobs, buckles and stringing.
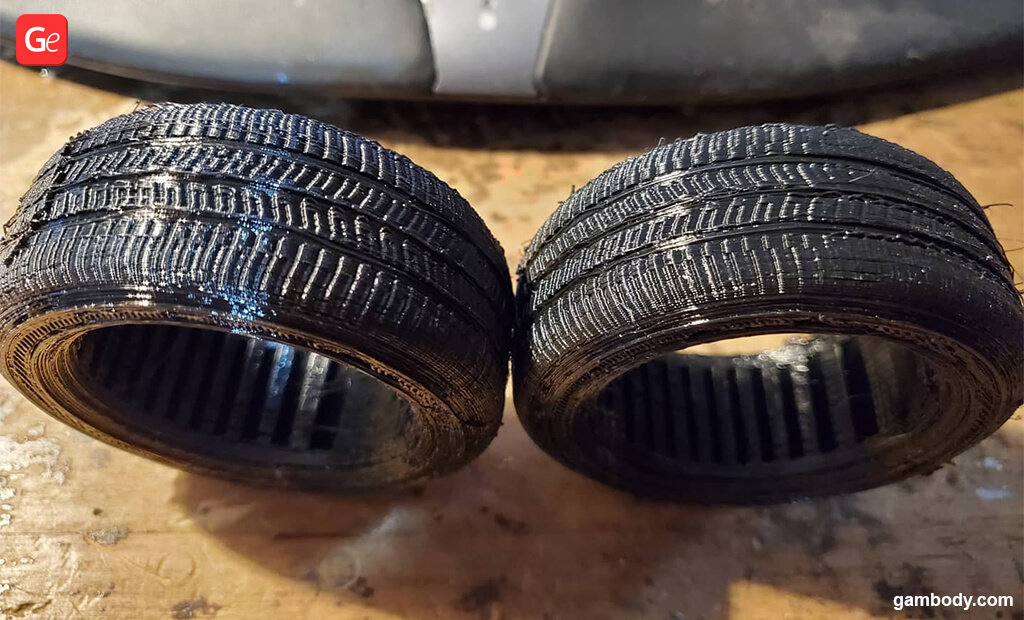

Some of the well-known rubber-like 3D printing materials are FlexSolid, NinjaFlex, FlexiFil, MatterHackers PRO Series Flex, Fila Flex and Soft PLA.
Flexible Filament Temperature
If you enjoy making fantastic figurines and models on a 3D printer, you should learn how to print flexible filament. TPEs are great to go with most FDM 3D printers. Still, this ‘naughty’ material requires particular features in a 3D printer, so make sure that your machine can work with thermoplastic elastomers.
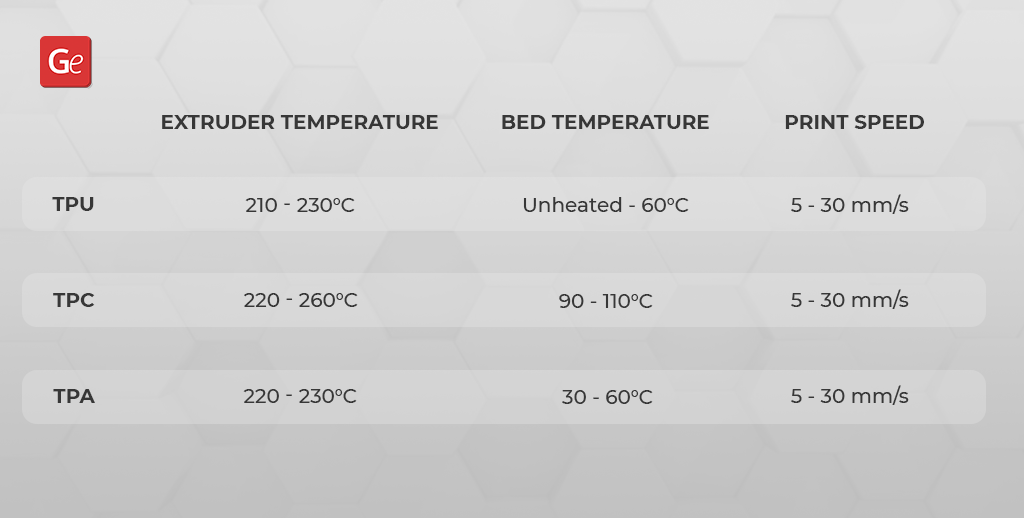
Here is the list of things you have to meet for printing flexible filament:
- Your 3D printer has a part cooling fan.
- Your heated bed reaches the temperature of 45-60 °C (113-140 °F) or gets higher for TPC.
- Your printer has PEI build plate, or you can use Painter’s Tape for bed adhesion.
- You have a direct drive extruder with a temperature of 225-245 °C (437-473°F).
Tips for Printing Flexible Filament
Follow Gambody’s tips for printing flexible filament if you wish to avoid such possible problems as stringing, clogging and ruined 3D prints.
1. Print at Slow Speed
Working with elastic 3D printing material can be a challenge, so following flexible filament printing tips is a must to enjoy a fantastic result. It is best to use slow speed and steady feed rate, which allows you to control the process and not turn TPE into a jam-like structure.
At high speed, the thermoplastic elastomers can easily compress and ruin your 3D print. Thus, when you are making wheels for a 3D printed car or something else that is rubber-like, it is great to experiment and find your perfect speed.
You might like to start printing at 20 mm/s speed and proceed to find your optimal settings. It is also a great idea to begin printing at 0.1mm – 0.2mm layer height.
2. Unwind Flexible Filament Downwards
It is easy to avoid possible flexible filament problems such as material stretching during the 3D printing process. You can adjust your workspace a little bit. When you mount the rubber-like spool on a 3D printer so that it unwinds automatically, the filament is pulled by extruder into the machine nozzle, and the TPE material is forced to stretch.
It is better to place the spool way above the 3D printing machine and unwind the material in a downwards direction. If you use a hub on a bearing, the material can also spin freely. This way, you can low down its resistance and achieve outstanding results, create stunning 3D printed models and figurines.
3. Disable Retraction
When you start to learn how to print flexible filament, it is better to adjust settings and turn off retraction feature in your 3D printing software. Newbies can make great 3D prints with thermoplastic elastomers when there are no retractions. Still, they will have to adjust their printing speed.
At the same time, advanced users can use retraction option but reduce the pressure in the nozzle and avoid numerous flexible filament problems this way. Lower retraction speed can help you prevent TPE stringing and blobs. If you are a fan of Simplify3D 3D printing software, you can also take advantage of one significant feature known as Coasting. It can reduce the pressure in the nozzle in one click.
4. Minimize Number of Retractions
If you choose to 3D print with retractions, follow our flexible filament printing tips to improve the quality of your printed models.
There is no need to select a straight path from one point to the other for a 3D printing model if you are working in Simplify3D. This software has a professional option designed for users who are in search of how to print flexible filament.

In the Advanced settings of the software, you can find ‘Avoid Crossing Outlines for Travel Movements.’ Enable this option, and the 3D printer would create a unique path that lows down the number of retractions and improves the quality of a 3D print.
5. Dry Flexible Filament
Keep in mind that TPEs absorb moisture. Thus, you have to learn how to dry flexible filament when you start working with this material.
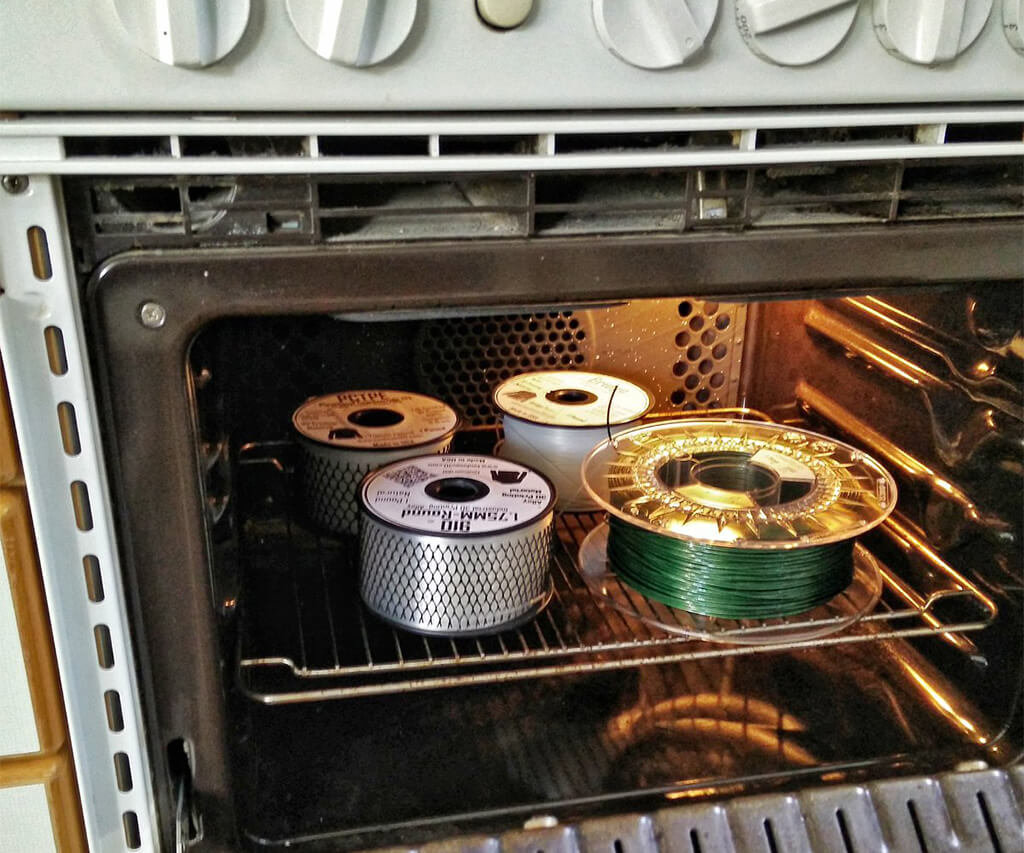

Firstly, learn how to store filament for 3D printing. Secondly, when you need to dry TPEs, use a conventional oven. Place the spool inside the oven at 57 °C (135 °F) and keep it there for 6 hours. Turn the heat off and let the flexible filament stay inside until the oven naturally cools down to the room temperature.
If you have a vacuum oven, follow a different guide on how to dry flexible filament. Place it inside this type of an oven for 30-60 minutes, and the material will be ready for 3D printing.
Never 3D print with wet TPE because this type of filament might sizzle and pop and ruin your 3D print.
6. Use Direct Drive Extruder
If your 3D printer comes with Bowden Extruder, you can try to 3D print flexible filament. However, it might not suit all types of TPE and cause the most common flexible filament problems, including the clogs and strings.
It is best to choose Bowden Extruder with calibration or Direct Drive Extruder, which can lead to fantastic results. It allows minimizing the distance between the drive and the hotend’s melt zone. This way, the flexible filament would be effectively fed into the nozzle.
Thanks to the remarkable tolerance of the pathway through which the thermoplastic elastomers pass into the melt zone, you can avoid such problems as kinking and coiling of the 3D printing material.
7. Follow Bowden Extruder 3D Printing Tips for TPE
If your 3D printer comes with Bowden Extruder, you can still create unique 3D prints with TPEs. Learn how to print flexible filament to avoid any issues.
Here are some tips to follow:
- Make sure the first layer sticks well by levelling your print bed and manually calibrating the corners;
- Use Blue Tape to attach the first layer but do not overheat the bed too much;
- Try using E-step calibration and find your best settings for printing with TPEs directly on the glass bed.
Best 3D Printer for Flexible Filament
As Gambody has noted, TPE is excellent to go with most FDM 3D printers. Which 3D printers are best for working with stretchy material? While you can adjust the settings of Bowden Extruder, it is still better to choose a machine with Direct Extruders.
For example, you can choose FlashForge Creator Pro priced at $700. It comes with dual extruder, direct drive, metal frame and many other features. It prints different materials, including flexible filament.
Other 3D printers you can look at are Monoprice Maker Select Plus (about $300) and QIDI-Tech X-Pro (approximately $600). The Monoprice machine boasts a big heated bed, Wi-Fi support, touchscreen and direct extruder. And the QIDI-tech machine comes with direct dual extruder, Wi-Fi support and an aluminium bed that heats up. Both 3D printers are suitable for printing flexible filament, and they give you full control over the machine settings.
Dremel 3D45 is more expensive. This machine costs way over $1,000. It includes a direct drive extruder, nice print bed and extra features such as Wi-Fi support and an HD camera that records the video of the 3D printing process. It supports various 3D printing materials. It works excellent with Dremel-made flexible filament, nylon, Eco ABS, etc. But many users manage to 3D print with other filament brands as well even though they are not officially supported.
Anyways, you can find your best 3D printer for flexible filament at different prices. Both affordable and expensive brands can work with TPEs and deliver outstanding results.
Gambody – Premium 3D printing marketplace hopes that our flexible filament printing tips will help you to create complex models and figurines with rubber-like parts easily. Remember to share the photos of your fantastic 3D prints with Gambody community on Facebook.



